In a world filled with sweet indulgences, imagine a life without the simple pleasure of savoring a delectable dessert or drizzling a spoonful of golden honey onto your morning toast. Sugar has long been regarded as a potential culprit in the development of diabetes, but what about honey? This naturally occurring sweetener, hailed for its unique taste and multitude of health benefits, has sparked an intriguing question: Can honey cause diabetes?

Nature’s alchemy unfolds within the buzzing confines of a beehive, where diligent bees gather nectar from vibrant flowers and transform it into a golden elixir known as honey. This liquid gold has been celebrated for centuries, adored for its rich flavor, tantalizing aroma, and captivating texture. With each spoonful of honey, we embrace the essence of nature’s bounty and unlock a world of culinary possibilities.
The link between honey and diabetes has been a subject of much speculation and conflicting opinions. While it is true that honey is a concentrated source of natural sugars, its impact on blood sugar levels and its potential to contribute to the development of diabetes require careful examination. To unravel the truth, we must delve into the depths of scientific research and separate fact from fiction.
Unveiling the Honey: Nature’s Golden Nectar
Nature’s alchemy unfolds within the buzzing confines of a beehive, where diligent bees gather nectar from vibrant flowers and transform it into a golden elixir known as honey. This liquid gold has been celebrated for centuries, adored for its rich flavor, tantalizing aroma, and captivating texture. With each spoonful of honey, we embrace the essence of nature’s bounty and unlock a world of culinary possibilities.
The Honey-Diabetes Connection: Fact or Fiction?
The link between honey and diabetes has been a subject of much speculation and conflicting opinions. While it is true that honey is a concentrated source of natural sugars, its impact on blood sugar levels and its potential to contribute to the development of diabetes require careful examination. To unravel the truth, we must delve into the depths of scientific research and separate fact from fiction.
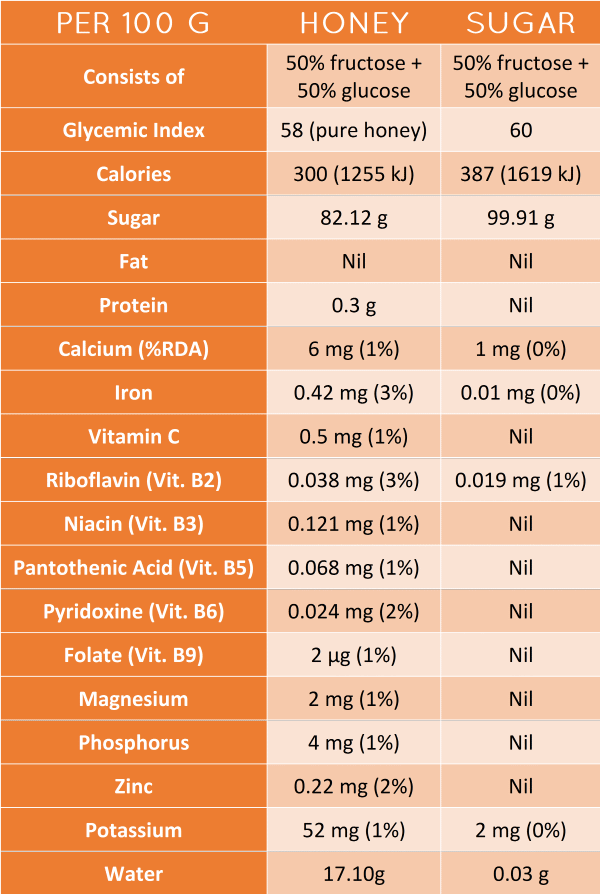
Honey’s Nutritional Composition: A Deeper Look
Beyond its irresistible sweetness, honey offers a complex nutritional profile that sets it apart from refined sugars. This natural wonder is composed primarily of fructose and glucose, the two simple sugars that provide its distinct taste. However, honey is not merely a source of empty calories. It also contains trace amounts of vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and antioxidants, making it a more wholesome alternative to processed sugar.
Honey’s Impact on Blood Sugar Levels: Separating Myth from Reality
One of the key concerns surrounding honey is its potential to raise blood sugar levels rapidly. However, scientific studies have revealed a more nuanced understanding of how honey affects our glucose metabolism. Unlike refined sugars, honey boasts a unique composition that allows for a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in a more gradual and controlled rise in blood sugar levels. This is attributed to the presence of fructose, which is processed differently by the body.
While honey may have a moderate impact on blood sugar levels, it is crucial to remember that individual responses can vary. Factors such as overall diet, lifestyle, and individual health conditions play a significant role in determining the effects of honey on blood sugar regulation. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
The Benefits of Honey: Potential Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Honey’s allure extends beyond its sweet taste. This natural elixir holds the promise of potential health benefits, thanks to its rich antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Certain varieties of honey, such as Manuka honey or raw, unprocessed honey, have been shown to possess higher levels of these beneficial compounds. Antioxidants help protect our bodies against oxidative stress, while anti-inflammatory properties may support overall well-being. However, it is important to note that further research is needed to fully comprehend the extent of these effects and their specific mechanisms.
Moderation is Key: Incorporating Honey into a Balanced Diet
As with any sweetener, moderation is key when incorporating honey into a balanced diet. For individuals with diabetes or those at risk, careful monitoring of carbohydrate intake, including honey, is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of honey to include in a diabetes management plan. Moderation entails understanding portion sizes and being mindful of overall carbohydrate intake from various sources, including fruits, grains, and other sweeteners. By practicing moderation, individuals can enjoy the natural sweetness of honey while maintaining a balanced and healthy diet.
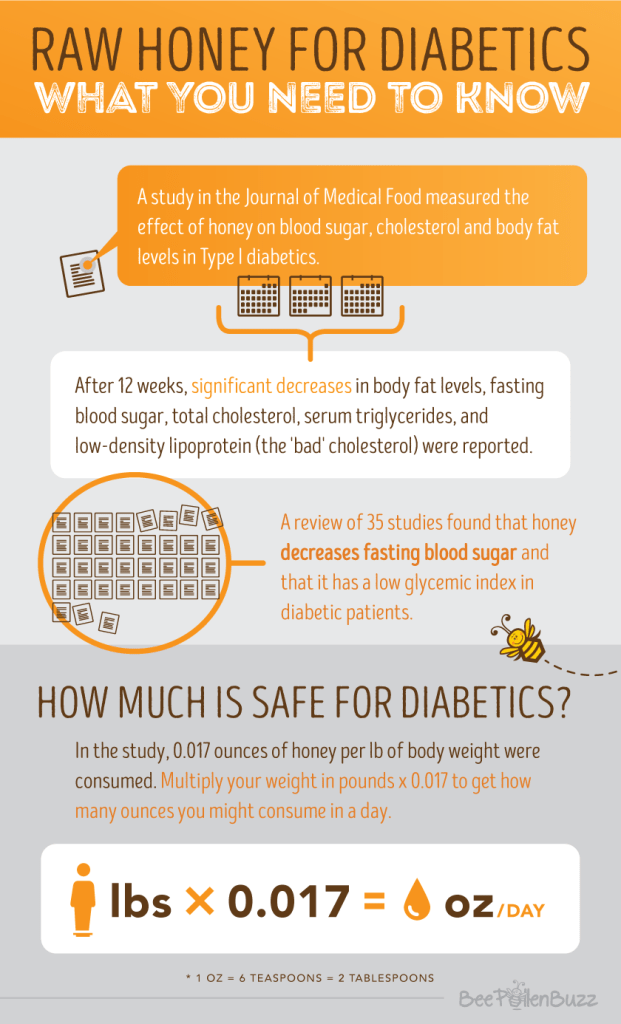
Conclusion: Savoring the Sweetness with Awareness
In the age-old debate of whether honey can cause diabetes, a more nuanced understanding emerges. While honey contains sugars, its impact on blood sugar levels differs from that of refined sugars. The unique composition of honey, with its blend of fructose and glucose, allows for a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream, potentially offering a more favorable glycemic response.
Moreover, honey boasts a range of nutritional benefits, including vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and potential anti-inflammatory properties. These qualities make it a more wholesome choice compared to processed sugars. However, it is essential to approach honey consumption with awareness, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Personalized dietary considerations, moderation, and guidance from healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in incorporating honey into a balanced diet.
So, can honey cause diabetes? The answer lies in understanding the intricate interplay between honey, blood sugar levels, and overall health. By embracing the sweetness of honey in moderation, accompanied by a diverse and balanced diet, individuals can savor its natural richness while maintaining a mindful approach to diabetes management.
As we navigate the intricate realm of nutrition, let us remember that our health is a harmonious symphony, where the sweetness of life can be relished with knowledge, awareness, and moderation.

