Spring and summer days are ideal for seeing bees flying over meadows. If we observe a bee in flight, we will see that it moves completely winding: up and down or left and right. And her flight is accompanied by a buzz.
While in flight, the wings of bees are almost impossible to spot, not because they are small and colorless, but because of the speed of movement.
Did you know? The rapid movements of the wings in collision with air particles produce longitudinal waves that we hear as the buzzing of bees.
In this article, you will find out how bees fly, how fast bees fly, how much time bees fly in a day, how fast a bumblebee can fly, how high bees can fly and many other interesting facts about bee flight.
Bee Wing Anatomy
Understanding bee wings is the key to discovering how bees fly. So let’s find out more about bee wings together.
The bee has two pairs of wings bound to the connecting membrane of the second and third rings of the chest. The wings have striped thickenings (veins) that strengthen them, and the trachea, blood and nerves pass through them. The front wing is larger than the rear. While resting, the wings are positioned along the body so that the front wing covers the rear.
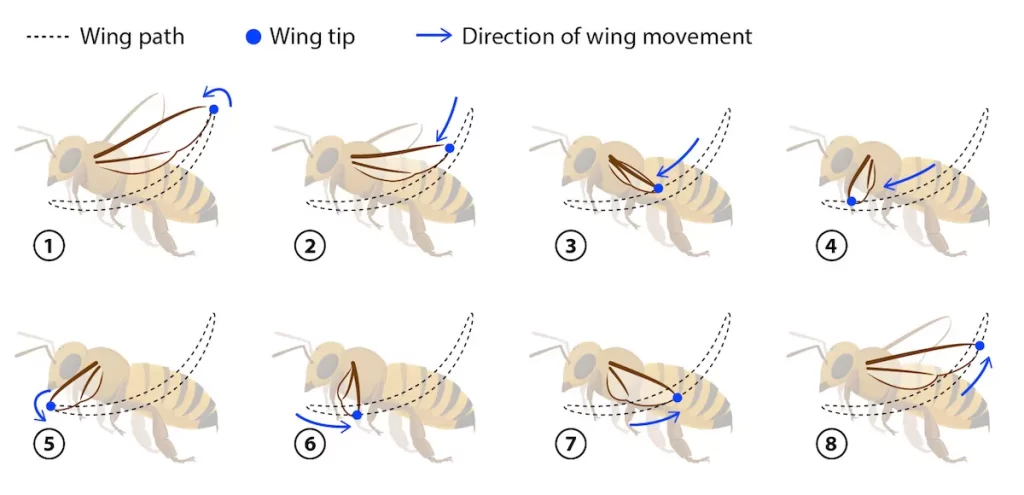
There is a row of teeth on the front edge of the hind wings. These teeth allow the two wings to act as one large surface and help the bee to create a greater lift during flight.
Read the article: How Bees Make Honey?
The wings themselves consist of three layers:
Transparent membranes at the top and bottom supported by a network of veins carrying hemolymph (bee “blood”), Nerves, Breathing tubes.
The wings move vertically and in a forward and backward direction so that the tips of the wings form the eight during flight. The wings are moved by two pairs of strong muscles located in the chest. The muscles do not grip the wings directly but the moving parts of the skeleton in which the wings are attached. One pair of muscles goes in the longitudinal direction and the other in the transverse direction. The drone has longer wings (11.5 mm) than both the worker bee (9.2 mm) and the queen (9.5 mm).
Here are the speeds of some of the most common bee species:
| Insect Type | Average Flight Speed | Fastest Flight Speed |
| Honey bee | 12mph | 20mph |
| Bumble bee | 7mph | 33mph |
| Yellow Jacket | 7mph | 30mph |
| Hornet | 14mph | 25mph |
How Do Bees Fly?
Now that we are familiar with the anatomy of bee wings we can write about bee flight, primarily how the bee flies.
Despite all the fascinating facts we know about bees, scientists are still confused as to how it is possible that such small wings can carry the body weight of a bee. The wings have been shown solely to give a sense of proportion.
But the secret is right in the wings. Their wings are not rigid and do not move only in an up-and-down motion. The wings of bees are flexible and can rotate. Their flight muscles allow the wings to rotate and twist during flight thus making swinging movements back and forth.
This movement creates enough lift to allow the bees to fly.
Interestingly, in flight, the bee’s wing makes over 400 swings per second.
How Fast Bees Fly?
Different species of bees have different flight speeds. How fast a bee can fly depends on several factors. Among them are:
❖ Presence or absence of nectar in goiter;
❖ Windy or quiet weather;
❖ What is the terrain that the bee needs to overcome.
The speed of the bee when leaving the hive is about 30 km per hour. In some sources you can find the figure of 40 and 60 km per hour. A bee with nectar flies slower, about 13-22 km per hour.
If the weather is windy, then the unloaded bee flies about 20 km per hour, while the bee with nectar in these conditions has a speed of 3-14 km per hour.
Read the article: Do Bees Sleep? Do Bees Sleep In Flowers?
How High Can Bees Fly?
According to some research, the height of bee flight without nectar is 10-11 m, and with nectar it is 5 m. If a strong wind blows, the bee descends lower to the ground. In this case the height above ground level is only 1 m.
How Far Can A Bee Fly?
How far the bees fly depends on where the plants are, from which nectar and pollen can be obtained. It has also been found that for more honey-bearing plants, the bee will easily go beyond the usual path.
In beekeeping, the term is mentioned – the useful radius of flight of bees. This is the distance that the bee flies towards the flower, spending the least effort and food. Such a flight is considered the most affordable and efficient. The useful radius is from 1 to 2 kilometers.
In order for a bee to have the strength to fly for food, it must have a supply of honey or nectar. Workers consume about 0.4 mg of product per kilometer of flight. A stuffed bee spends food on producing energy from the nectar it collects from flowers. A stuffed bee consumes more food than is unloaded.
Therefore, the more times she flies out of the hive, the more food she consumes on the way home.
Beekeepers should be aware of the notion of useful radius before setting up an apiary at an ideal distance from the field with honey plants. Another option is to purchase mobile hives that can be delivered directly to the nectar collection site.
How Much Time Do Bees Fly Per Day?
The working day of the worker bees starts at 4-5 in the morning. Bees go to work at the time of flower opening. They return to the hive to sleep at 20-21 o’clock. Sometimes bees that do not have time to return home during the day spend the night on plants.
On average, a flight in search of food takes from 20 minutes to 1 or 2 hours. Returning to the hive, the bee that brings food spends 8-16 minutes there. This time is spent on handing over the collected products to the receiving bees. Upon completion of the transfer, the worker bee leaves the hive again.
As a result, the bee manages to make 7-11 flights a day. During each flight to the plant and back to the family, bee flies an average of 4 to 10 km. As a result, a small insect travels 40-100 km in one working day.
Read the article: Does Honey Expire And Does Honey Go Bad?
How Do Bees Fly In Different Conditions?
Time is a factor that greatly influences the movement of bees. Bees will prefer to hide in hives in case of rain, strong winds, or foggy weather; high or too low temperatures.
The best time for bee activities is a sunny day without wind or with a light breeze.
On too humid, cold or hot days, the amount of nectar in plants decreases significantly. Therefore, rainy summers can disrupt the life of bee communities. In this case, the flying individuals do not go for food, and the bees that process pollen and nectar have no work.
Most species of bees fly during the day. Therefore, a large number of bees do not fly at night because they cannot see and avoid obstacles.
How Fast Do Bumblebees Fly?
Bumblebees fly thanks to two wings located on the front of the body.
It has long been believed that a bumblebee can fly contrary to the laws of physics. Indeed, a massive body carried on one pair of small wings is a rather unusual sight. However, physicist Jane Wang from the American University managed to prove that there is nothing surprising in flying bumblebees.
The speed of the bumblebee is 4 m / s. The wings produce up to 300-400 movements per second
The whole secret is that insects not only flutter their wings, but also rotate them (like helicopters), producing 300-400 movements per second.
Read the article: Does Honey Freeze? What Happens When You Freeze Honey?
More Interesting Facts
❖ One bee visits about 10 flowers per minute and one trip from the hive takes about 10 minutes. So during one flight the bee visits about 100 flowers. Outside the hive, the bees work 6-7 hours a day. During that time they make about 40 flights and visit about 4,000 flowers.
❖ The effect of worker bees in nectar collection is greater when grazing is close and flights are shorter. If the collection location is 1 km away from the apiary, the bees will return to the hive with a full load in 3-5 minutes, while they will travel 3 km in 20-25 minutes. For 1 kg of honey, bees need to bring about 140,000 loads of nectar.
❖ The bee can fly away from the hive for almost 8 km and will find its way back without a mistake. However, the working distance of the bee should not exceed 2 km.
❖ During flight, the bee’s wing makes over 400 swings per second.
❖ For a flight period of 20 days, the bee can bring 6-8 g of nectar, from which 3-4 g of honey is obtained.

