Introduction: Decoding the Mystery of Bee Communication
Bees are incredible insects known for their complex social structure and remarkable communication skills. Have you ever wondered how these tiny creatures manage to coordinate their activities and work together as a cohesive unit? In this blog post, we will explore the fascinating world of bee communication, shedding light on their unique language and signaling methods.
Bee communication is essential for their survival and successful foraging. Through various dances, pheromones, and signals, bees convey crucial information to their colony members. Join us on this journey to unravel the secrets of their communication system.
What Are Bee Dances and How Do They Convey Messages?
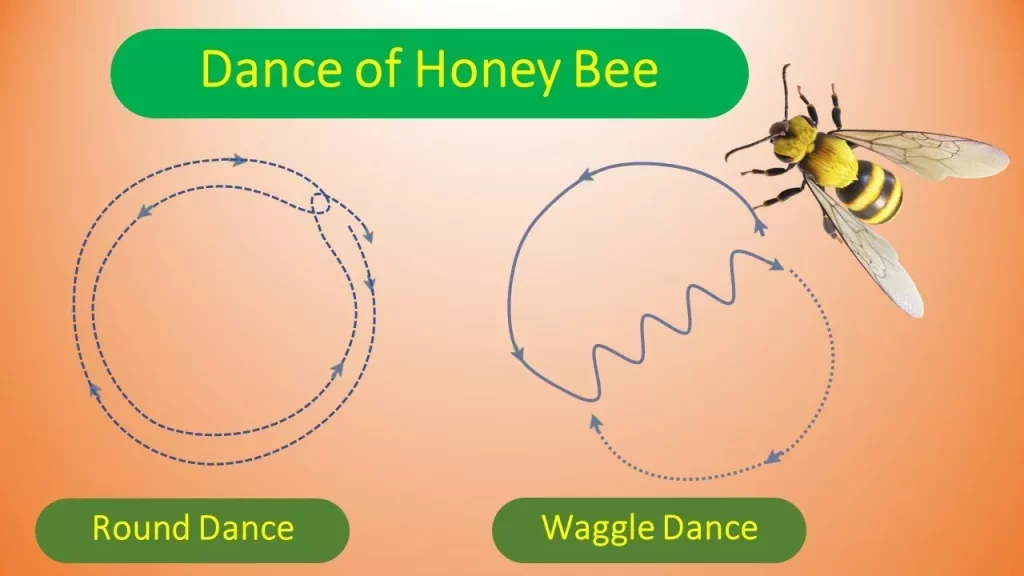
One of the most famous forms of bee communication is the “Waggle Dance.” This intricate dance involves bees moving in specific patterns to convey valuable information about the location of food sources. By analyzing the duration, direction, and intensity of the waggle dance, other worker bees can precisely navigate to the food-rich areas.
In addition to the waggle dance, bees also use “Round Dances” to communicate the presence of nearby food sources. The round dance is characterized by rapid, circular movements and indicates that the food is within a short distance from the hive.
Unraveling the Waggle Dance: A Dance of Directions
The waggle dance is a sophisticated language unique to honeybees. When a foraging bee returns to the hive after discovering a rich food source, it performs the waggle dance to inform other bees about the location. The dance’s angle in relation to the sun represents the direction, while the duration of the dance indicates the distance to the food.
| Dance Angle | Direction | Interpretation |
| 0° – 30° | Straight Upward | Food is located in the direction of the sun |
| 30° – 90° | Right of Upward | Food is located to the right of the sun |
| 90° | Right Horizontal | Food is located directly to the right |
| 90° – 150° | Right of Downward | Food is located to the right of the sun |
| 150° – 180° | Straight Downward | Food is located in the opposite direction |
By decoding the waggle dance, bees can efficiently exploit food sources and ensure the survival of their colony.
The Importance of Bee Pheromones in Colony Communication
Besides dances, bees rely heavily on pheromones to communicate within the colony. Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by bees that convey specific messages to other individuals. These chemical signals play a vital role in organizing the hive’s activities and maintaining social harmony.
How Bees Use Pheromones to Organize and Signal Within the Hive
| Pheromone | Purpose |
| Queen Mandibular Pheromone (QMP) | Released by the queen to maintain colony cohesion and suppress worker reproduction. |
| Brood Pheromone | Produced by brood cells and keeps worker bees caring for the young brood. |
| Alarm Pheromone | Signals danger or threats, alerting other bees to respond accordingly. |
| Nasanov Pheromone | Used during orientation flights to help returning bees locate their hive entrance. |
The coordinated release of these pheromones ensures smooth hive functioning and supports the division of labor among worker bees.
Foraging Communication: How Bees Share Information About Food Sources?
Effective foraging communication is critical for the success of a bee colony. Once a bee discovers a new food source, it returns to the hive and communicates the location and quality of the food to other bees through dances and pheromones. This enables efficient exploitation of resources and ensures the survival of the colony during challenging times.
The Intricate Social Structure of Bees and Its Role in Communication
Bees live in highly organized and well-structured societies. Their social structure is divided into different castes, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
- Queen Bee: The queen is the heart of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the hive’s population.
- Worker Bees: These female bees perform various tasks like foraging, nursing, building, and defending the hive. They are the backbone of the colony and participate in most communication activities.
- Drone Bees: Male bees that mate with the queen. They do not have stingers and do not participate in hive activities.
The clear division of labor and communication between these castes contribute to the hive’s efficient functioning.
Bee Communication: Exploring Insect Methods Beyond the Hive
While bees are famous for their hive-based communication, other insect species also use fascinating methods to convey information.
For instance, ants utilize pheromone trails to guide other colony members to food sources. Termites communicate through head-banging to signal danger. These diverse methods showcase the complexity of insect communication in the natural world.
Navigating Nature: How Bees Communicate and Find Their Way Home
Bees are exceptional navigators. They use a combination of visual cues, the sun’s position, and the Earth’s magnetic field to orient themselves during flights. This impressive navigational ability allows them to return to the hive accurately, even after extensive foraging trips.
Understanding Bee Communication Research: Recent Discoveries and Insights
Scientific research continues to unveil the intricacies of bee communication. Studies have shown that bees can adapt their dances and signals to changing environmental conditions, demonstrating their remarkable cognitive abilities.
Researchers are also exploring the impact of human activities on bee communication and how this may affect their survival and pollination efforts.
Bee Communication and Pollination: A Vital Link for Ecosystems and Agriculture
The significance of bee communication extends beyond the hive. Bees play a crucial role in pollination, facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants and supporting diverse ecosystems. Additionally, they contribute significantly to agricultural productivity by pollinating crops, ensuring food security for humans and other animals.
The Human Connection: How We Interpret and Learn from Bee Communication
Studying bee communication not only provides insights into the natural world but also offers valuable lessons for human societies. Observing how bees cooperate, communicate, and adapt to changes can inspire us to build more sustainable and interconnected communities.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity and Beauty of Bee Language
In conclusion, the intricate language of bee communication is a marvel of nature. Through dances, pheromones, and signals, bees effectively coordinate their activities and ensure the survival of their colonies. Understanding and appreciating this complex system can foster a deeper connection with the natural world and inspire us to protect these incredible pollinators.
Next time you see a bee buzzing around a flower, take a moment to marvel at the extraordinary communication happening right in front of you.
Remember, bees communicate in ways we are still uncovering, so let’s continue to explore, research, and protect these vital creatures for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – How Do Bees Communicate?
Q: What is the significance of bee communication within a hive?
A: Bee communication is vital for the survival and productivity of a bee colony. Through dances and pheromones, bees convey essential information about food sources, threats, and hive organization, ensuring efficient division of labor and resource exploitation.
Q: How do bees perform the famous “Waggle Dance”?
A: The “Waggle Dance” is an elaborate dance performed by foraging bees to communicate the location and quality of food sources. The dance’s direction and duration indicate the distance and direction of the food relative to the position of the sun.
Q: What other dances do bees use for communication?
A: Apart from the “Waggle Dance,” bees also use “Round Dances” to communicate the presence of nearby food sources. The round dance involves rapid, circular movements and signifies that the food is within a short distance from the hive.
Q: How do bees use pheromones to communicate?
A: Bees rely on chemical signals called pheromones to convey specific messages within the hive. These chemical substances are secreted by bees and play roles in maintaining colony cohesion, regulating worker behavior, and signaling danger.
Q: What are the different roles within a bee colony’s social structure?
A: A bee colony’s social structure consists of three main castes: the queen bee, worker bees, and drone bees. The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while worker bees handle tasks like foraging, nursing, building, and defending the hive. Drones are male bees that mate with the queen.
Q: How do bees navigate and find their way back to the hive?
A: Bees are excellent navigators and use a combination of visual cues, the sun’s position, and the Earth’s magnetic field to orient themselves during flights. This impressive navigational ability allows them to return accurately to the hive after foraging trips.
Q: How do bees contribute to pollination and its significance?
A: Bees play a crucial role in pollination by facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants. This process is essential for maintaining diverse ecosystems and supporting agricultural productivity, ensuring food security for humans and other animals.
Q: How can understanding bee communication benefit humans?
A: Studying bee communication provides valuable insights into the natural world and offers lessons for human societies. Observing how bees cooperate, communicate, and adapt to changes can inspire us to build more sustainable and interconnected communities.
Q: What ongoing research is exploring bee communication?
A: Scientists are continuously studying bee communication to uncover more details about their language and the impact of environmental changes. Research is also focused on understanding the cognitive abilities of bees and their responses to various stimuli.
Q: How can individuals contribute to protecting bees and their communication system?
A: To protect bees and their communication system, individuals can create bee-friendly gardens with native plants, avoid using harmful pesticides, support local beekeepers, and spread awareness about the importance of bees in ecosystems and agriculture.
Q: What can we learn from bee communication to apply in our daily lives?
A: Bee communication teaches us the value of effective communication, cooperation, and adaptability. Applying these principles in our daily lives can foster better relationships, efficient teamwork, and a deeper appreciation for nature and its wonders.

